Understanding the Relationship Between Supply and Demand
In every kind of market - whether it’s onions at your local shop or the cost of a shiny new gadget - one core connection drives everything behind the curtain: supply affects demand, yet demand tugs right back on supply. These forces bend price tags, set limits on availability, plus guide what businesses choose to do next. See how they react to each other? Suddenly, all this cash-related stuff starts making real sense.
What Are Supply and Demand?
Demand’s merely what people want - though only pay up for some.
When plenty of people want a thing, it shows more desire. But if only a few care about it, wanting fades fast.
Demand shows what shoppers are after but also able to afford.
When businesses produce lots of a product, it becomes easier to find. Yet when production falls behind, stock levels go down.
Pretty straightforward, right?
How Supply and Demand Interact
This is when things begin to feel interesting. When supply moves, it’s because demand tugged first - like steps matching in rhythm, each motion tied to the last.
1. When Demand Increases but Supply Stays the Same
Prices go up.
Here's the deal - when people want more but there’s no extra stuff available, they start competing, which pushes prices higher. Think about festive seasons: demand spikes outta nowhere, so costs shoot up quick.
2. When Demand Decreases but Supply Stays the Same
Prices fall.
Once people stop buying something quick, stores usually slash prices - simply to clear out inventory. This is precisely how sales periods play out.
3. When Supply Increases but Demand Stays the Same
Prices drop.
If a bunch of tomatoes flood the market fast, sellers get stuck with too many - so buyers don’t want to spend big, which drags prices down.
4. When Supply Decreases but Demand Stays the Same
Prices rise.
When stock gets low - maybe storms hit - but buyers still grab items, prices go up. Though conditions worsen and shopping continues, expenses increase too. As supply shrinks while desire holds steady, fees get higher regardless. If weather causes issues but demand stays flat, vendors bump rates anyway.
Equilibrium: The Point Where Supply Meets Demand
When supply hits demand dead-on - that’s where pros call equilibrium. Things level out here: no surplus hanging around or gaps showing up - flow stays smooth
Shoppers leave happy with their cash going toward something meaningful
Sellers are happy 'cause they’re making cash
The market keeps moving at a steady pace
Out there, though, things keep shifting because when supply shifts, demand also moves along.
Why This Relationship Matters
Figuring out their link helps you see - here’s the reason
Petrol prices rise or fall
Phones get cheaper after a while
Next time something's low-price, soon after you'll see prices jump up
Firms decide how much to produce depending on expected sales
It affects buyers, businesses - while steering how leaders decide to respond.
A Simple Example
A brand-new gaming console lands in shops. Because everyone wants one, but the company only made a handful, people can't find it easily.
High demand
Low supply
Result: Very high prices
A few weeks later, they began pushing harder - ramping up quick
Supply increases
Demand becomes stable
Result: Prices drop to normal
This loop pops up everywhere - like when you're growing crops or tinkering with devices.
Conclusion
The connection between supply and desire shapes every part of how money moves. Yet it doesn’t sit quiet - constantly changing, pulling here or there, nudging prices while steering where deals go. Once you grasp that flow, everyday things - say food at the store or plane ticket rates - start clicking, all tied to that one core notion.

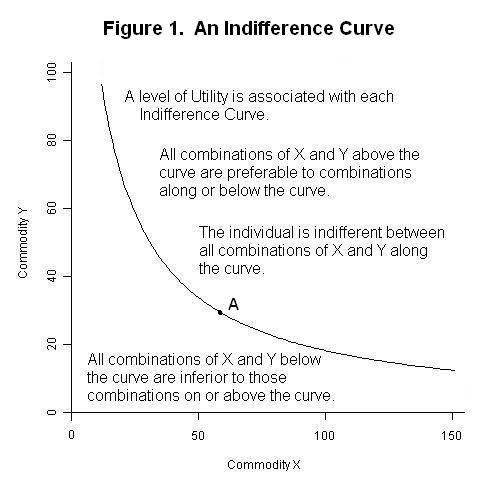
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/marginalutility-cff85ddfd620484f8afbf9d3f6cf4b74.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TermDefinitions_Utility-e42a7528caa347f9b1af149065ab2b9d.jpg)