⚖️ Problems of Deficient and Excess Demand and Their Corrective Measures – Class 12 Economics
Ever noticed how sometimes there’s too little demand for goods, and businesses struggle to sell — while at other times, prices shoot up because everyone’s buying more than what’s available?
These are two sides of the same coin in economics — Deficient Demand and Excess Demand.
Let’s break this down simply and clearly.
💡 Meaning of Aggregate Demand (AD)
Before we understand the two problems, let’s quickly recall what Aggregate Demand means.
Aggregate Demand = The total demand for all goods and services in an economy during a given period.
It includes:
👉 Consumption (C)
👉 Investment (I)
👉 Government expenditure (G)
👉 Net exports (X – M)
So, AD = C + I + G + (X – M)
When AD doesn’t match the economy’s full employment level of output, problems arise — either deficient or excess demand.
📉 Deficient Demand
🔎 Meaning:
Deficient demand occurs when aggregate demand is less than the aggregate supply at the full employment level.
In simple words — people are not spending enough, businesses don’t sell enough, and production slows down.
💥 Causes of Deficient Demand:
- Decrease in consumer spending (due to low income or savings)
- Decrease in investment (due to low business confidence)
- Fall in government expenditure
- Decrease in exports
- Increase in taxes (reduces disposable income)
⚠️ Effects of Deficient Demand:
- Fall in output and employment
- Recession in the economy
- Deflationary pressure (prices fall)
- Wastage of resources
- Low profit and business closures
💊 Measures to Correct Deficient Demand (Deflationary Gap):
The government and central bank use expansionary policies to increase demand.
🏛️ 1. Fiscal Measures (by Government):
- Increase government spending on infrastructure, education, etc.
- Reduce taxes so people have more disposable income.
- Increase transfer payments like pensions, subsidies, and scholarships.
💵 2. Monetary Measures (by Central Bank):
- Reduce the bank rate → cheaper loans for businesses.
- Lower Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) → banks can lend more.
- Buy government securities (OMO) → increases money supply.
🧠 Goal: Encourage spending, raise investment, and bring the economy back to full employment.
📈 Excess Demand
🔎 Meaning:
Excess demand occurs when aggregate demand exceeds aggregate supply at full employment level.
It means people are spending too much, but there aren’t enough goods and services available.
💥 Causes of Excess Demand:
- Increase in consumer spending (higher income or optimism)
- Increase in investment (due to low interest rates)
- Rise in government expenditure
- Increase in exports
- Decrease in taxes (leaves people with more money)
⚠️ Effects of Excess Demand:
- Inflation (rise in prices)
- Over-utilization of resources
- Trade deficits (imports rise)
- Mal-distribution of income (rich get richer)
- Boom conditions that can lead to economic instability
💊 Measures to Correct Excess Demand (Inflationary Gap):
The government and central bank use contractionary policies to reduce demand.
🏛️ 1. Fiscal Measures (by Government):
- Reduce government spending
- Increase taxes to reduce disposable income
- Reduce transfer payments
💵 2. Monetary Measures (by Central Bank):
- Increase bank rate → loans become expensive
- Raise CRR and SLR → banks lend less
- Sell government securities (OMO) → reduces money in circulation
🧠 Goal: Control inflation and bring demand back to sustainable levels.
⚖️ Comparison: Deficient vs Excess Demand
| Basis | Deficient Demand | Excess Demand |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | AD < AS at full employment | AD > AS at full employment |
| Nature | Deflationary gap | Inflationary gap |
| Prices | Fall | Rise |
| Employment | Unemployment | Over-employment |
| Policy Type | Expansionary | Contractionary |
🧠 Conclusion
Both deficient demand and excess demand are harmful to the economy — one causes unemployment, the other brings inflation.
That’s why governments and central banks constantly try to maintain a balance using fiscal and monetary tools.
In short — too little demand slows growth, and too much overheats the economy.
The key is to keep Aggregate Demand = Aggregate Supply at the full employment level.
✍️ Quick Recap
| Problem | Effect | Corrective Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Deficient Demand | Recession, Unemployment | Expansionary Fiscal & Monetary Policy |
| Excess Demand | Inflation, Overheating | Contractionary Fiscal & Monetary Policy |
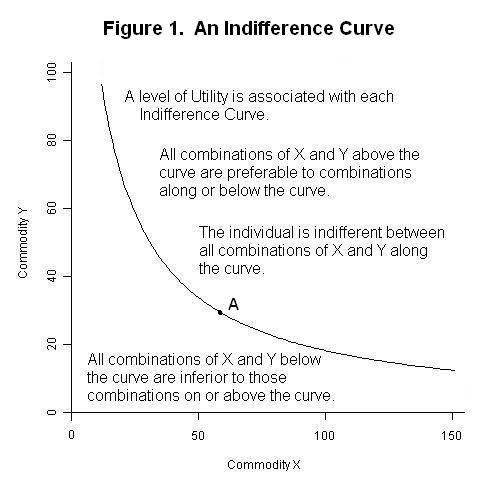
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/marginalutility-cff85ddfd620484f8afbf9d3f6cf4b74.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TermDefinitions_Utility-e42a7528caa347f9b1af149065ab2b9d.jpg)