Forms of Market and Price Determination in Different Markets
Markets are more than just places where buyers and sellers meet — they are systems where prices are determined, goods and services are exchanged, and economic activity is coordinated. The way a market functions depends on its structure, the number of participants, and the nature of the product being sold.
Economists classify markets into different forms, each with its own way of determining prices. Let’s explore these forms and how prices are set in each.
1. Perfect Competition
- Features:
- Large number of buyers and sellers
- Homogeneous (identical) products
- Free entry and exit of firms
- Perfect knowledge about prices and products
- No government interference in price setting
- Price Determination: Price is set purely by the forces of demand and supply. Individual firms are price takers, not price makers. The equilibrium price is where the market demand curve intersects the market supply curve.
- Example: Agricultural produce markets (e.g., wheat, rice in open wholesale markets).
2. Monopoly
- Features:
- Single seller in the market
- No close substitutes for the product
- High barriers to entry for other firms
- Firm has full control over supply
- Price Determination: The monopolist is a price maker. Price is set where the monopolist’s marginal cost (MC) equals marginal revenue (MR). Monopolists often charge higher prices and restrict output compared to competitive markets.
- Example: Indian Railways (in passenger rail transport), patented medicines.
3. Monopolistic Competition
- Features:
- Many sellers
- Differentiated products (branding, quality, features)
- Some control over price
- Relatively free entry and exit
- Price Determination: Prices are influenced by product differentiation and brand loyalty. Firms have some degree of price-making power, but competition limits the extent. Prices can be higher than in perfect competition but lower than monopoly.
- Example: Restaurants, clothing brands, cosmetics.
4. Oligopoly
- Features:
- Few large firms dominate the market
- Products may be homogeneous or differentiated
- High entry barriers
- Strong interdependence among firms
- Price Determination: Prices are often stable because firms may avoid price wars. Price may be determined through collusion (cartels) or non-price competition (advertising, quality improvements). In some cases, a price leader firm sets the market price.
- Example: Automobile industry, telecom sector, soft drink companies.
5. Duopoly
- Features:
- Only two dominant sellers
- High interdependence in decision-making
- Products may be similar or differentiated
- Price Determination: Price changes by one firm directly affect the other. Firms may compete aggressively or form a tacit agreement to keep prices stable.
- Example: Aircraft manufacturing (Boeing & Airbus globally).
Summary Table – Market Forms and Price Determination
| Market Form | No. of Sellers | Product Type | Price Setter/Taker | Price Determination Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perfect Competition | Many | Homogeneous | Price taker | Demand & Supply equilibrium |
| Monopoly | One | Unique | Price maker | MC = MR |
| Monopolistic Competition | Many | Differentiated | Limited price maker | Brand value + competition |
| Oligopoly | Few | Homo/Diff | Price maker (interdependent) | Collusion or price leadership |
| Duopoly | Two | Homo/Diff | Interdependent | Mutual influence on pricing |
Conclusion
The form of market determines how much control a seller has over pricing. In perfect competition, prices are market-driven, while in monopoly, a single firm dominates. Monopolistic competition adds brand-based variation, and oligopoly brings strategic decision-making into the mix. Understanding these forms helps consumers, businesses, and policymakers make informed economic decisions.
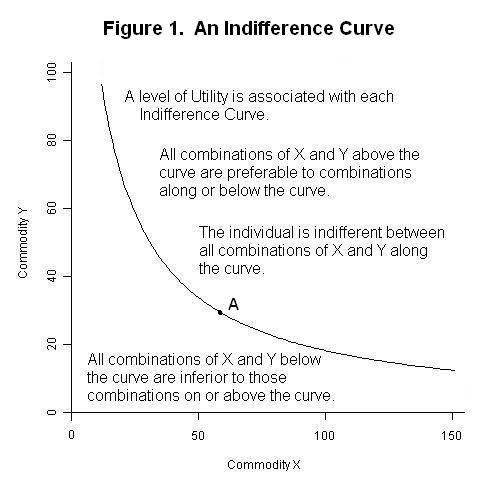
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/marginalutility-cff85ddfd620484f8afbf9d3f6cf4b74.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TermDefinitions_Utility-e42a7528caa347f9b1af149065ab2b9d.jpg)