Theory of Consumer Behaviour – Class-12
Understanding why people buy what they buy isn’t just economics — it’s basically understanding human nature. The Theory of Consumer Behaviour tries to answer a simple question:
How do consumers make choices when their wants are unlimited but their resources (mainly income) are limited?
Every day, knowingly or unknowingly, we make choices — tea or coffee, bus or cab, branded shoes or budget ones. Economics studies these decisions to understand patterns and create models that explain consumer behaviour.
Why Consumer Behaviour Matters
Consumers cannot have everything they desire. So, they make choices based on:
- Preferences
- Budget
- Utility (satisfaction)
The theory helps businesses set prices, governments frame policies, and students like you understand how choices work in real life.
Key Concepts in Consumer Behaviour
1. Utility
Utility means satisfaction a consumer gets from consuming a good.
There are two types:
- Total Utility (TU): Total satisfaction from consuming various units.
- Marginal Utility (MU): Extra satisfaction gained by consuming one more unit.
The logic is simple:
The first bite of pizza feels amazing. The second is also good. By the fourth or fifth, you’re like… okay, that’s enough.
This is where Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility kicks in.
2. Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
This law states that as more units of a good are consumed, the additional satisfaction keeps decreasing.
It explains why:
- You won’t pay the same price for the 5th slice of cake.
- Consumers prefer variety.
- Discounts work on bulk purchases.
3. Budget Set
A consumer’s income is limited.
The budget set includes all combinations of goods that a consumer can afford with their given income and prices.
For example:
If you have Rs 200, you’ll choose a combination of goods that fits within that amount.
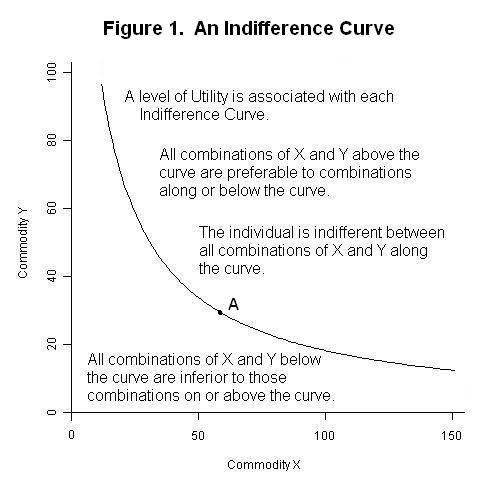
4. Indifference Curve
An indifference curve shows combinations of two goods that give the same level of satisfaction.
Features:
- They slope downwards (if one good increases, the other must decrease).
- They never intersect.
- Higher indifference curves represent higher satisfaction levels.
This is a more realistic approach compared to utility numbers because it focuses on preferences.
5. Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS)
MRS tells you how many units of one good a consumer is willing to give up in exchange for one more unit of another good, while keeping satisfaction same.
For example:
How many packets of chips would you sacrifice for an extra chocolate bar?
6. Consumer’s Equilibrium
A consumer is in equilibrium when they reach the highest possible indifference curve within their budget.
In simple words:
Best possible choice under money limits.
The condition for equilibrium:
- MRS = Price Ratio
This means the consumer’s willingness to substitute goods equals the market’s rate of substitution (based on prices).
Real-Life Example
Imagine you have Rs 300 and you want to buy burgers and cold drinks.
You think:
- How much satisfaction each extra burger or drink gives you.
- How much of each you can buy with Rs 300.
- Which combination gives you maximum satisfaction.
Your final choice (say 2 burgers + 1 cold drink) is your consumer equilibrium.
Why This Theory Is Important
- Helps understand how people spend money.
- Helps businesses decide product pricing and combos.
- Helps governments predict demand and supply trends.
- Helps students develop logical thinking.
Conclusion
The Theory of Consumer Behaviour is more than just diagrams and formulas. It’s about understanding how real people behave when faced with choices. Since resources are limited and wants are unlimited, consumers always try to choose the mix of goods that gives them the highest satisfaction within their budget.
Once you understand these concepts — utility, budget sets, indifference curves, and equilibrium — the entire chapter becomes a lot more relatable and easier to remember.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/marginalutility-cff85ddfd620484f8afbf9d3f6cf4b74.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TermDefinitions_Utility-e42a7528caa347f9b1af149065ab2b9d.jpg)