Coordination Compounds: Understanding the Chemistry of Complexes
Chemistry doesn't just involve basic stuff like H2O or CO2. Now and then, atoms link up in ways that get kind of messy. This is when coordination compounds show up - strange setups you'll spot in things like blood cells or factory-grade helpers.
Here's how we can look at each one without getting confused.
What Are Coordination Compounds?
A coordination compound - also known as a complex - usually has a metal ion or atom at its center, bonded to nearby molecules or ions referred to as ligands.
Imagine the metal ion's like the leader, while the ligands stick close to it, kind of like crewmates following orders.
A standard setup usually appears as follows:
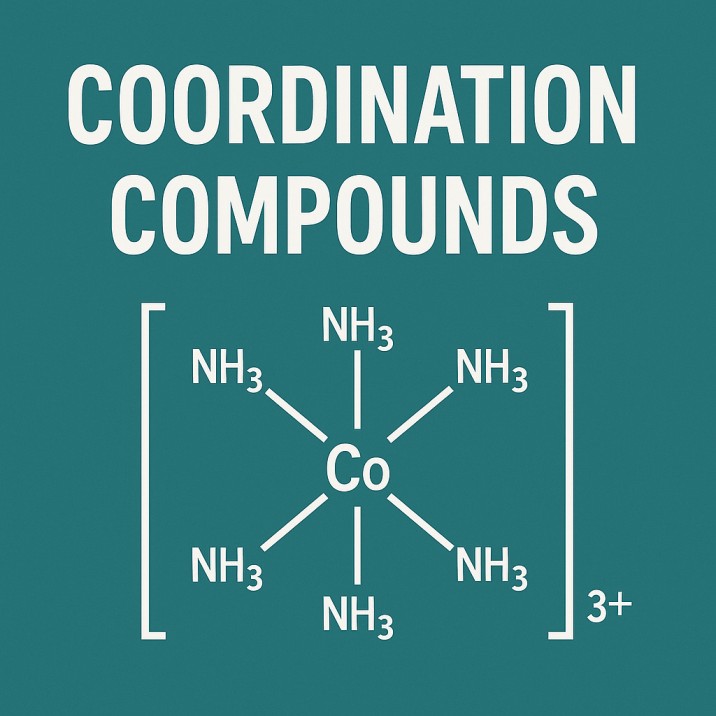
³⁺
Cobalt sits right at the core
NH₃ acts as the ligand - there are six attached
Such substances usually sit within squared marks "", making it easier to spot the entire structure as one piece.
Why Are They So Important?
You might not notice, yet coordination compounds pop up just about anywhere:
In people’s bodies – hemoglobin’s got a combo deal where iron (Fe²⁺) sits right in the middle.
In plants - chlorophyll, needed for making food from sunlight, centers around magnesium.
In medicine – cisplatin, known for fighting cancer, happens to be a coordination compound too.
In factories – Common for coating metals, making colors, speeding up reactions, or pulling out pure elements.
Fundamentally, if there were no coordinated substances, living things wouldn't seem anything like they do now.
Key Terms You Should Know
To get your head around this subject without trouble, check out these key words you should know:
1. Central Metal Atom/Ion
Typically a metal such as cobalt, iron, or nickel - though sometimes it’s an element from another group. Instead of sticking to just one category, these materials might come from broader parts of the periodic table.
2. Ligands
These are ions or molecules that donate electron pairs to the metal.
These might fall into categories like:
Monodentate – bind through one donor atom (e.g., Cl⁻, NH₃, H₂O)
Bidentate means attaching via two separate donor sites - like how ethylenediamine works
Polydentate means it attaches at several spots - like how EDTA works
3. Coordination Number
How many parts of the molecule stick to the metal center.
Some folks pick 4 - others go for 6.
4. Coordination Sphere
Inside the square brackets - that’s where you find the core metal along with its surrounding ligands.
5. Oxidation Number
Figure out the metal's charge once you subtract what the attached groups contribute.
How Do Coordination Compounds Form?
These come together by shared electron pairs from molecules linking up with metals in special bonds.
The metal ion lacks electrons, so it easily takes them in.
This leads to steady forms with distinct shapes such as:
Octahedral
Tetrahedral
Square planar
These forms straight-up affect traits like hue, how they react, or magnetic behavior.
Properties of Coordination Compounds
1. They Show Beautiful Colors
Different ligands shift the light's wavelength that gets soaked up, so the complexes end up showing bold colors.
This happens because of electron shifts between orbitals.
2. Variable Magnetic Behavior
Based on how electrons pair up, a substance might become:
Paramagnetic (unpaired electrons)
Diamagnetic (all paired)
3. Isomerism
Like carbon-based molecules, metal complexes can come in different forms that look alike but aren't quite the same
Structural isomerism (linkage, coordination, ionization)
Stereoisomerism (geometrical & optical)
4. Stability
Different ligands make complexes more or less stable in their own way.
EDTA sticks tightly to lots of metals, making solid bonds that don’t break easy.
Applications That Affect Everyday Life
Take a look at these genuine, everyday situations:
A solution with silver and ammonia plays a key role in creating shiny mirror surfaces.
[Fe(CN)₆]⁴⁻ helps make blue dyes, like Prussian blue.
EDTA combos pull toxins like lead out of your blood.
Catalysts - such as the one made by Wilkinson - lend a hand when building organic molecules.
Yep, those chemicals aren't stuck in books - instead, they're quietly used across tons of fields.
Wrapping Up
Coordination compounds might look tricky at first - yeah, that was intentional - yet after grasping the core concept, like a central metal hooked to surrounding molecules, things begin making sense. These structures play key roles across nature, healthcare, manufacturing, even in how living systems function.
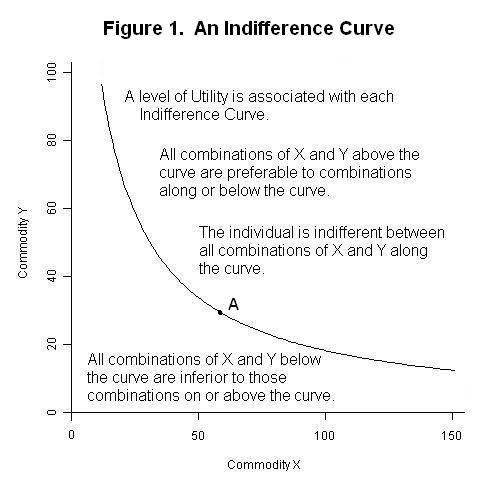
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/marginalutility-cff85ddfd620484f8afbf9d3f6cf4b74.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TermDefinitions_Utility-e42a7528caa347f9b1af149065ab2b9d.jpg)